In the business world, the term ‘Attrition’ is used to describe the gradual and unpredictable reduction or dwindle of a vital resource or crucial stakeholder group. There are mainly two types of attrition that businesspeople must be well-apprehended about, they can be either:
Employee Attrition: This type of attrition refers to the reduction of staff members of a company due to unavoidable consequences such as resignation, retirement, permanent sick leaves or death of employees; these reductions are not followed by the recruitment of fresh employees.
Customer Attrition: This type of attrition refers to the defection or churning of the customer base to result in a reduction of the client base in a company. This type of attrition can transpire due to the loss of interest, moving on, ageing of customers or less attraction by new customers.
Evaluating Attrition in a company
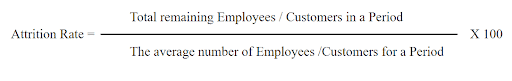
Evaluating the rates of attrition allows the employer to comprehensively explore ways to control labour costs by freezing the hiring processes to save money incurred on retired employees; it basically provides the raw business closure that any company must envision when understanding the company’s actual performance rates. When it comes to customers, the company can utilise the customer attrition statistics to apprehend the actual figures of loyal customers and the company products’ or services’ propensity to attract new customers. This will allow the organisation to find new ways to retain customers and attract new customers cost-efficiently. Here are some benefits of evaluating attrition rates in a company:
- You can understand the precise factors that affect your employees’ satisfaction
- You will be granted with competitive compensation
- You can evaluate attrition to reorganise your business efforts
- You can understand the rate of your ageing workforce- soon-to-be-missed expertise and loyalty
- You can use this information to review human capital and ensure business continuity by disposing of unnecessary costs
The Disparity between Employee Attrition and Employee Turnover
Employee Attrition does not address the action taken by an employer to replace the ex-employees with new recruits and directly refers to the elimination of the particular asset or position via a ‘hiring freeze’ after the employees terminate from serving a company. Therefore, Employee Attrition is very distinctively from Employee Turnover, because, Employee Turnover refers to the after-action taken by the employer to replace the vacant positions of the company after an employee ceases providing his or her services due to retirement, resignation or any other reason to terminate from working for the company or division.
Since attrition can result in overflowing employee workload or depriving you of on-prem movement or promotional opportunities, you have to be well-versed about your employee attrition statistics at all times. Also, a shrinking client base can affect you detrimentally; therefore, you must learn about your customer attrition rates and figure out how you can fit-in to the disruptions and innovation in vogue. Thus, understanding attrition allows you to have a rigid presence in your marketplace and unshaken confidence in your employees’ retention.






